SWPIT
Energy harvesting (EH) technique has recently drawn significant attention, owing to its capability of prolonging the lifetime of energy constrained wireless networks, such as Internet of Things (IoT), wireless sensor networks (WSNs) and wireless body area networks. It enables wireless nodes to collect energy from the surrounding environment. Apart from the conventional renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, radio frequency (RF) signals radiated by ambient transmitters can be treated as a viable new source for energy harvesting.
One of most important application of RF-EH is simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT), which jointly use the RF signal to transfer both energy and information. It provides a potential possibility to tradeoff information-energy rate. Several transmitter-receiver architectures were proposed using time-switching (TS) and powers splitting (PS), see Figure 1.
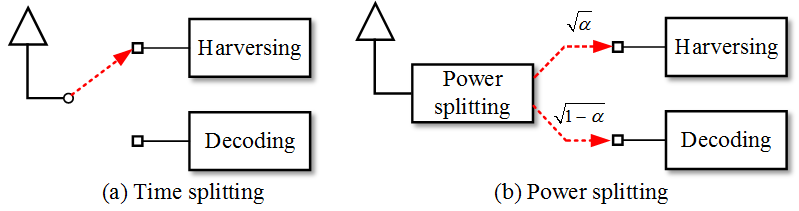
Achievable rate-energy analysis, which tradeoff the maximum information transmission rate with transmit power constraint, offers a promising alternative to design proper time splitting ratio or power splitting for practical communication system. On top of that, considering the coded modulation of signal allows a more efficient symbol-level splitting, which assign redundancy or the symbol with larger power for energy harvesting and assign the information or the symbol with less power for information decoding.
Project Description
Although the above-mentioned aspects of SWIPT are very attractive, there are many difficulties need to be investigated to jointly consider information decoding (ID) and energy harvesting (EH)
(1) The power sensitivity requirement level is different for RF information decoding and energy harvesting, such as Wireless energy receiver requires -10dBm and wireless information receiver requires -60dBm. It is possible that some transmitted symbols can activate the RF-EH circuit but others cannot.
(2) The modulation performance is different for ID and EH, such as high peak to-average power ratio (PAPR) leads to a better EH performance (M-PAM performs better than M-PSK and M-QAM), but it’s not good for information transmission (the ID performance of M-PAM is worse than M-PSK).
Therefore, it is necessary to derive an accurate analysis for the effect of different SWIPT receiver architectures and modulation scheme in the performance transmission rate for SWIPT system. This involves couple of research activities, which are listed below.
1) Analysis the achievable rate-energy region of different SWIPT receiver architectures (PS, TS)
2) Investigate and implement efficient modulated splitting and redundancy splitting schemes to address better information-energy rate.
3) Evaluation of the developed SWIPT receiver architectures in different energy constrained wireless networks.
Environment
You will be working in the ICT Lab of the Signal Processing Systems (SPS) Group, TU/e Eindhoven.
Your Background
Your basic signal processing background should be enhanced with knowledge about wireless communication and information theory. Course 5LSF0, “Applications of Information Theory�, Q4, provides this extra knowledge.
Contact

Interested applicants may contact:
Dr. Bin Chen (b.c.chen@tue.nl) or Prof. Frans Willems (f.m.j.willems@tue.nl).